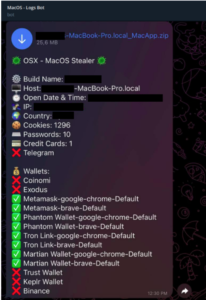
Install Tools
The attacker will use a couple of different tools to perform the man in the middle attack.
The attacker will absolutely need Ettercap and Wireshark to get the attack up and running. See the Ettercap page for the apt-get list of things you’ll need if you’re installing Ettercap from source.
The attacker may want to use Driftnet to analyze traffic during the attack.
Install these using your method of choice – package manager or source.
Ettercap: ARP Poisoning
The next step is to actually perform the ARP poisoning with Ettercap. Start the Ettercap GUI with the command
$ ettercap -G

Sniffing Type in Ettercap
Now we’ll specify the type of sniffing we want Ettercap to do.
Ettercap can either sniff in Bridged mode or Unified mode. These names refer to the configuration of the network devices on the attacking computer. Bridged mode means the attacker has multiple networking devices, and is sniffing as traffic crosses a bridge from one device to another. Unified is good for a single network device, where the sniffing and forwarding all happens on the same network port.
We’ll be doing unified sniffing. Select Sniff > Unified Sniffing from the menu.

Finding Hosts in Ettercap
Once we’ve picked our sniffing method, we need to pick a target and then start our attack.
We can run a quick scan of different hosts acting as parties in network traffic. Click Hosts > Scan for Hosts to run a quick scan and get a list of host targets. You should see Ettercap populate a list of host IP and MAC addresses.

Select Ettercap Poison Target
Now that you have a list of hosts, find your target in the list and click on it. (Or, if you want to attack every computer on the network, don’t select any list item.)
Start MITM Attack
Click Mitm > Arp Poisoning to select the Arp Poisoning attack.
This will print a message letting you know that the ARP Poisoning attack is beginning. As interesting/juicy information shows up on the wire, Ettercap will extract it and display it, just in case you don’t capture it or find it with Wireshark.

Make sure and check “sniff remote connections” before you start the attack.

Wireshark for Traffic Analysis
Now fire up Wireshark so that we can do a packet capture of our MITM session. Start a capture on the eth0 network interface (which is a network cable connected to the router, the same router that the sheep is connected to).
Test Wireshark Sniffing
Once the packet capture has started, we can test out Wireshark’s abilities to sniff out regular traffic. By running an ARP Poisoning MITM, we are able to see all traffic to the Sheep as though we were physically sitting at the same network port as them.
Test browse some unencrypted websites on your Sheep computer. Take a look at the Wireshark dumps. You should see a whole bunch of GET requests and traffic between the target and the destination:

Test Wireshark Credentials Sniffing
Sniffing login credentials and other interesting information that passes through unencrypted is also possible with Wireshark.
Find a website that requires login credentials, but that uses HTTP and not HTTPS. This should not be too hard (unfortunately).
Log in to this service using your login credentials. Make sure the Wireshark capture is still running in the background.
Once you’ve successfully logged in, you can stop the capture and look for your login credentials in the capture file.
Finding Login Credentials in Wireshark
First, before digging through the Wireshark capture file, double check to see if Ettercap was able to detect the login credentials. If so, you should see the username and password that you used to log in to the service in the clear in Ettercap’s information box.
Now let’s see how ti find the login credentials with Wireshark. What we’re looking for is an HTTP packet that corresponds to a request sent from Jupiter (the sheep) to the server containing login credentials for the server to check. We can narrow down our search with the following WIreshark search criteria:
ip.src==10.0.0.75 and http
By entering this in the filter bar at the top of the Wireshark window, we drastically cut down on the amount of traffic that we need to go through.
The packet we’re looking for is a request for a login page – perhaps login.php or something similar. Now we just look for a packet, sent from the client to the server, with the login page as the URL, and with an HTML Form chunk of data included in the packet. The username and password will be in clear text in the HTML Form data:

What ARP Poisoning Looks Like in Wireshark
Arp poisoning, of course, is a very loud and easily-detectable process, particularly when ARP poisoning a computer that is not taken off of the network. This will cause duplicate ARP entries, and the router will complain when this happens. Because these ARP packets are sent every few seconds, it would be easy to get a very detailed record of when the ARP poisoning happened, what network it happened on, and how long it lasted.

Driftnet for Image Traffic Analysis
One of the neat tools you can use in a man in the middle attack is Driftnet, which will automatically search the stream of web traffic and pick out images and stills from video, and show them to you. This is a quick way to get a visual sense of what a target is up to during a man-in-the-middle attack.
HTTPS/SSL
Let’s talk about how to deal with HTTPS during an ARP poisoning man-in-the-middle attack.
If you are using Ettercap, and let Ettercap handle the SSL certificates, they will be phony and invalid, and will raise suspicion with the sheep.
To avoid these kinds of warnings, we can use SSLStrip.
Using SSLStrip
SSLStrip is a service that will transparently hijack an HTTP session, and every time there is an HTTPS redirect or an HTTPS link, it will turn that into its HTTP equivalent.
This allows an attacker to force a sheep onto HTTP connections instead of HTTPS connections.
This will only affect links and redirects, however. It will not force HTTP if the target actually types “https://” in the browser address bar.
Using Firewall
We’ll set up a firewall rule that will search for any traffic bound for port 80, and redirect it to the port that SSLStrip is listening on.
$ iptables -t nat -A PREROUTING -p tcp --destination-port 80 -j REDIRECT --to-port 6666
and to make sure it worked, list your rules:
$ iptables --list -t nat
Or, remove all your rules:
$ iptables --flush -t nat
So now we have a firewall rule that directs any traffic destined for port 80 to port 6666, where SSLStrip waits for it.
Start SSLStrip
Now that we have our firewall rule, we can start SSLStrip:
$ sslstrip -l 6666
Perform MITM with Ettercap
Now that you’ve got your firewall rule for port 80, and your SSLStrip instance listening, run your ARP poison attack with Ettercap, e.g. attacking 10.0.0.1 and 10.0.0.75:
$ ettercap -T -q -i eth0 -M arp /10.0.0.1/10.0.0.75/
What I’m Seeing
On the Sheep end, seeing a lot of problems.
First, HTTPS sites give site certificate warnings. As expected.
But HTTPS links and redirects are not being handled correctly by SSLStrip.
When I do accept the phony certificate, the sites load but are all broken.
Warnings
Making the Sheep Suspicious
When using this method of MITM in a naive way, the user is apt to notice. Each time they visit an HTTPS site, they will see a warning notifying them that the site’s certificate couldn’t be verified.
The sheep will see this message on every HTTPS page they visit, so after a few times they would become suspicious that they were being attacked.
To beat this problem, you can use SSLStrip in your MITM attack, which allows you to only create ONE warning notifying the user that the site certificate could not be enabled. Once they accept and store that exception, even once, then you are home free. Every SSL connection the Sheep makes from that point forward will check to make sure the certificate presented is trusted, which it always will be. Any secure connection the Sheep attempts to make after that point can be compromised by that attacker.
Setting Off Intrusion Detection
If a network is administered, if anyone monitors anomalous network traffic, or if any intrusion detection/prevention systems (IDPS) are in place on the network, the attack will be immediately discovered. ARP poisoning is very easy to spot when looking at a packet capture:

Notice all of the messages stating “Duplicate use of 10.0.0.75 detected!” These are sent out every few seconds.
Duplicate Traffic
When you conduct a MITM attack, on a wired network your computer will be forwarding every packet that is not destined for it – meaning there will be lots of duplicate traffic generated by an attacker, which will show up as swarms of black packets:

An alternative method to ARP poisoning would be using a physical network tap.
See MITM/Wired/Network Tap
Protecting Yourself
Using HTTPS (Partial Protection)
Now we will switch to the scenario where you are the Sheep. What can you do to protect yourself from wolves performing MITM attacks?
One way to protect yourself against an ARP cache poisoning attack is to use HTTPS. Firefox extension HTTPS Everywhere can help – more info at the Anonymous Browsing page.
Using HTTPS prevents a MITM attacker from being able to sniff the contents of your traffic, and makes it much, much more difficult to spoof the endpoint. The traffic is now protected by math, instead of by network routes. Spoofing a MAC address or packet source is very easy – but spoofing a crypotgraphic key is difficult.
Browsers will also warn when HTTPS certificates are fishy (expired, suspicious, for the wrong domain, or not signed by a trusted root certficiate authority).
HOWEVER, understand the limitations of this protection.
During an MITM attack, a Sheep machine would not be able to establish HTTPS connections with outside websites, because every certificate presented by an attacker would have to be spoofed (an correctly spoofing a certificate is mathematically hard). So, the browser will show a warning about invalid certificates on every site:

There is a danger in accepting (even by accident) that invalid certificate, since Firefox would permanently store that certificate as a trusted certificate. Each time you visit any site via HTTPS, the forged certificate would be presented, and Firefox would silently accept the attacker’s certificate because it is trusted.
The moral is, never accept invalid certificates, ever, unless you trust your connection.
What HTTPS Does Not Protect
HTTPS encrypts your traffic. HTTPS does NOT obfuscate the destination of the traffic. Using HTTPS, the destination of your traffic is NOT hidden.
Let’s look at an example: when I fire up the Jupiter server, the sheep in the MITM attack, and I visit https://en.wikipedia.org and I log in with my MediaWiki username and password, an attacker performing a MITM attack will mainly just see traffic passing between Jupiter and a certificate authority (multiple IP addresses, but all registered under Verisign, a Certificate Authority.) I cannot sniff any packets going to external addresses because those are going through HTTPS tunnels that Wireshark doesn’t “see”.
HOWEVER, an attacker can still see the destination of HTTPS traffic!!! While your traffic consists almost entirely of TCP packets between you and a certificate authority (IP addresses owned by Verisign), there is one key packet that an attacker may look at to see the destination of your HTTPS traffic by looking through a Wireshark traffic dump: the “Server Hello, Certificate, Server Hello Done” packet.

When you open this packet in Wireshark, you will see the packet contains a certificate. This is the certificate coming from the server, to whom the request is going to. In the photo above you can see clearly that despite the Sheep’s use of HTTPS, someone performing a man-in-the-middle attack can still sniff the Sheep’s connection.
Here’s another example: I fired up Jupiter, a sheep in a man-in-the-middle attack. I visited an https website (htts://www.travelocity.com). I saw the warning about the certificate. I accepted the certificate. I logged into the HTTPS site.
I was not running anything other than Ettercap. I wanted to see what plain HTTPS traffic looks like to a sniffer.
First thing, if I filter on the IP address of the sheep and look at the DNS requests being sent, the destination of the HTTPS traffic can be seen in the clear:
(A long lost image: File:WiresharkEttercapDns.png)
HTTPS is a way of encrypting the contents of HTTP packets. It doesn’t affect DNS packets, or TCP packets, or any other kind of traffic other than HTTP.
HTTPS traffic will protect the contents, but NOT the destination, of your traffic.
Plus, HTTPS can be beat during a man-in-the-middle attack using SSLStrip.
HTTPS with Tor can protect the contents of your HTTP traffic and anonymize the destination of the HTTP traffic. Anonymous Browsing
Watch the Network for Telltale Signs
Some telltale signs that an ARP Cache poisoning attack is happening:
- Repeated broadcast messages indicating two computers report having the same IP address
- ARP packets sent out to other computers coming from somewhere other than the router
- Unusual ARP packet activity
Basic Tutorial for Newbies
It only works on HTTP Websites
open ettercap
click on Tick Mark and go to “…” and then Hosts and then Scan for Hosts
Then click on “…” again and then host lists
172.20.10.1 first one is always the router
72.10.10.11 is my Testing Device Iphone
Router Add to Target 1 and my testing device Iphone and other target devices to Target 2
Click on MTM Menu globe icone and click ARP poisoing and click ok.
visit any http website on the wifi network and login using any detail
it will come to ettercap like below
GROUP 2 : ANY (all the hosts in the list)
Host 172.20.10.1 added to TARGET1
Host 172.20.10.11 added to TARGET2
HTTP : 44.228.249.3:80 -> USER: TinkoMinko PASS: chunumunuu INFO: http://testphp.vulnweb.com/login.php
CONTENT: uname=hii&pass=hii
On wireshark
On HTTPS websites, you can only view the websites they are visiting, not the content on if or the details you enter.
ip.src== 172.20.10.11 and dns in Wire Shark to find all the websites that testing iphone is viewing.
Disclaimer
- Neither the project nor its developer promote any kind of illegal activity and are not responsible for any misuse or damage caused by this project.
- This project is for educational purpose only.
- Please do not use this tool on other people’s devices without their permission.
- Do not use this tool to harm others.
- Use this project responsibly on your own devices only.
- It is the end user’s responsibility to obey all applicable local, state, federal, and international laws.


 Ethical Hacking/Pen Testing3 years ago
Ethical Hacking/Pen Testing3 years ago
 Vulnerabilities/Malwares3 years ago
Vulnerabilities/Malwares3 years ago
 Malwares3 years ago
Malwares3 years ago
 Ethical Hacking/Pen Testing3 years ago
Ethical Hacking/Pen Testing3 years ago
 Windows/Mac/Linux4 years ago
Windows/Mac/Linux4 years ago
 Cyber Attacks/Data Breaches4 years ago
Cyber Attacks/Data Breaches4 years ago
 Mobile Hacking3 years ago
Mobile Hacking3 years ago
 Ethical Hacking/Pen Testing3 years ago
Ethical Hacking/Pen Testing3 years ago